(LOWER BACK WORKOUTS INCLUDED!)
The best lower back exercises for strength and muscle growth will help you build lower back strength and avoid injuries.
If I asked you to name the best back exercises, what would you say? If you’re like most, you’ll immediately mention bent-over rows and lat pulldowns. You might even throw in rear deltoid exercises like the rear delt fly and a traps exercise like the shrug. What’s missing here?
How do you build lower back strength?
The lower back is an often neglected area when it comes to strength and muscle growth. Most people focus so much on the bigger and more popular exercises, completely forgetting that the lower back plays an equally important role if you want to build a powerful core, strong posterior chain, and achieve a perfectly balanced physique. And keeping the back strong is one of the best ways to best ways to fix lower back pain.
Put simply, you can’t ignore your lower back during your weekly workouts. In this article, we’ll discuss the anatomy and function of the lower back muscles along with the best lower back exercises for strength and muscle growth, no matter what type of fitness equipment you have available to you.
Key Points
- To enhance the connection between your mind and the lower back muscles, it is essential to comprehend their placement in relation to each other as well as how they work.
- It’s important to understand the proper acute variables related to your specific fitness goals. The sets, reps, and rest breaks for strength are different for muscle growth.
- For strength, you should perform 2 to 3 exercises each workout for the target muscle along with 4 to 6 working sets of 5 to 7 reps at 75% to 85% of your one-repetition maximum.
- For muscle growth, you should aim to perform 2 to 3 exercises each workout for the target muscle along with 3 to 5 sets of 8 to 12 reps at 65% to 75% of your one-repetition maximum.
- To guarantee continuous development and prevent hitting a plateau, overload is non-negotiable. After all, working out with the same routine for months will inevitably lead to a standstill.
- No matter how hard we strive to achieve our fitness goals, it won’t mean anything if we don’t give our muscles the time they need to repair and recover. To make sure that each workout session makes an impactful difference in your life, prioritizing rest and recovery is a must.
- The best supplements for lower back muscle growth and recovery include whey protein, creatine monohydrate, free-form EAAs, and sleep supplements including zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D.
Anatomy and Functions of the Lower Back Muscles
Several muscle groups make up the lower back. Understanding the location of these muscles and how they function is important so you can improve the mind-to-muscle connection with them.
Multifidus
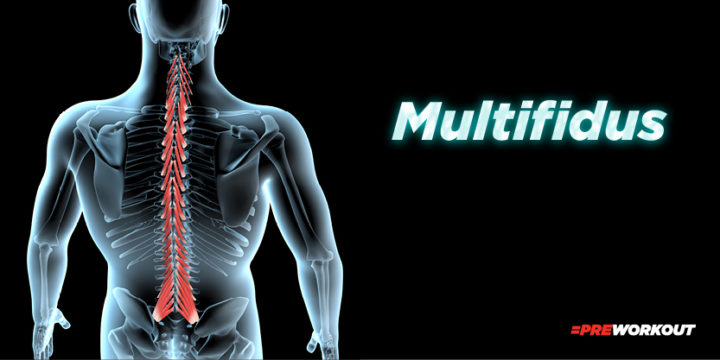
Belonging to the group of spine extensors, the multifidus runs along the entire length of the spine. It is the deepest of the lower back muscles and helps with stabilization, posture, flexion, and extension.
The multifidus handles the stabilization of your spine and does so by contracting to keep it in proper alignment and prevent injuries during lifting or other strenuous activities.
Erector Spinae
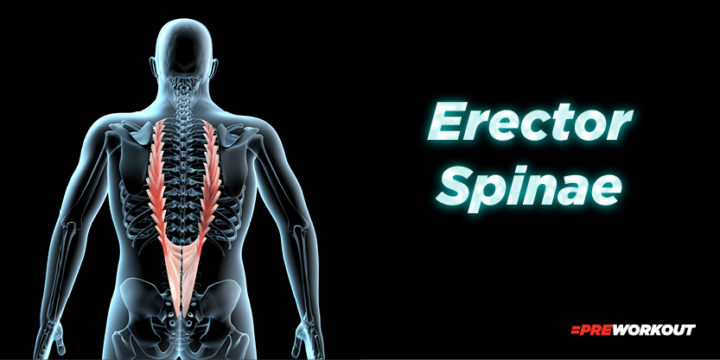
The erector spinae are also in the spine extensor category, and its primary function is to maintain upright posture. It originates from the sacrum and runs up to the cervical vertebrae, forming a sheath around the spine.
Spinalis
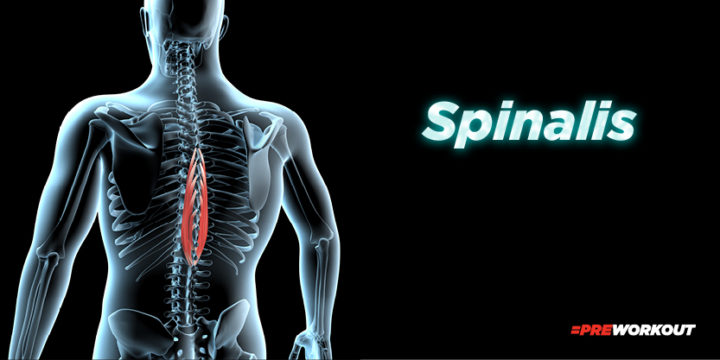
Located beneath the multifidus and consists of two parts – the thoracis, which is responsible for spinal flexion and extension, and the cervicis, which helps with neck rotation.
Besides helping you maintain proper posture, this muscle group also contributes to torso stabilization through its connection to various abdominal muscles. It also helps with posture and stability by contracting to maintain proper alignment of the spine.
Latissimus Dorsi
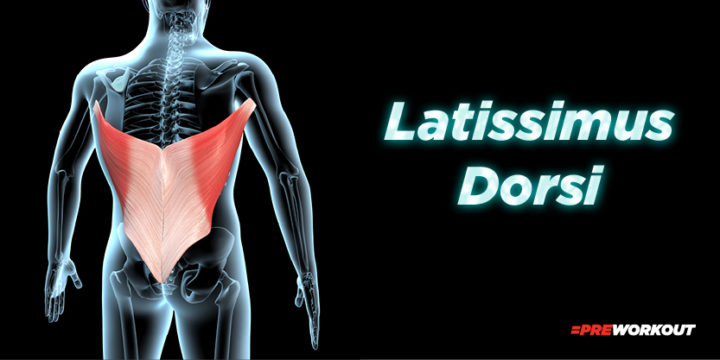
It might feel strange to think of the lats as a lower back muscle, but there’s a reason they are dubbed the “wings of the back.”
The lats are the biggest muscles on your back, and they start from the waist and go up, crossing over several vertebrae before branching out to the upper-middle back.
The lats help with shoulder flexion and extension, as well as spinal stabilization when you are lifting heavy weights and performing exercises such as pull-ups.
How To Progressively Overload the Lower Back for Hypertrophy & Strength
To maximize strength or muscle growth in your lower back, you’ll need to progressively overload the muscles.
First, you need to make sure you’re utilizing the proper acute variables for your goals of strength and hypertrophy.
Acute variables are the sets, repetitions, tempo, etc. that you’ll be doing for each lower back exercise and workout. But these numbers are crucial as they are like the roadmap for building the body you want.
Acute Variables for Strength
- Exercises: Perform 2 to 3 exercises each workout for the target muscle
- Sets: 4 to 6 working sets (not including warm-up sets)
- Repetitions: 5 to 7
- Load: 75% to 85% of your one-repetition maximum (1RM)
- Tempo (Time Under Tension):
- Concentric (lifting the weight): 1 seconds
- Isometric (pausing at the top): 1 seconds
- Eccentric (lowering the weight): 3 seconds
- Rest Time: 90 to 120 seconds [1] [2]
Acute Variables for Muscle Growth
- Exercises: Perform 2 to 3 exercises each workout for the target muscle
- Sets: 3 to 5 (not including warm-up sets)
- Repetitions: 8 to 12
- Load: 65% to 75% of your one-repetition maximum (1RM)
- Concentric (lifting the weight): 2 seconds
- Isometric (pausing at the top): 0 seconds
- Eccentric (lowering the weight): 2 seconds
- Tempo (Time Under Tension):
- Rest Time: 60 to 90 seconds [2] [3]
How to Use Progressive Overload
As the name suggests, progressive overload is a method used to gradually increase the stress on the target muscles. Overload is essential for continuous progress because using the same workout for months will eventually lead to a plateau.
Here are some of the best ways to smash through (or avoid altogether) a plateau:
- Increasing the weight so the last two reps feel very challenging
- Increase the number of sets
- Increase the number of reps, assuming it falls in line with your goals
- Maximize the time under tension by holding the weight longer
- Perform drop sets on the last set of an exercise
- Perform the advanced progression of the exercise
- Use the one-leg or single-sided variation of an exercise [4] [5]
The key here is to find what works best for you and tweak it along with your exercises so as not to hit plateaus in muscle growth.
Be sure to evaluate your progress and update your workout accordingly every four to six weeks.
Best Lower Back Exercises with Dumbbells
How do you strengthen your lower back with dumbbells? Try the below exercises.
- Romanian Deadlifts
- Bent-Over Rows
- Single Arm Dumbbell Row
- Dumbbell Back Extensions
- Dumbbell Aquaman
Best Bodyweight Lower Back Exercises
- Supermans
- Bird Dogs
- Glute Bridge
- Back Extensions
- Single-Leg Romanian Deadlifts
Best Barbell Lower Back Exercises
- Deadlifts
- Barbell Rows
- T-Bar Rows
- Rack Pulls
- Good Mornings
Best Cable Machine Exercises for Lower Back
- Seated Cable Rows
- Pull-Throughs
- Single Arm Lat Pulldowns
- Straight-Arm Pulldowns
- Cable High Pulley Rows
Resistance Band Lower Back Exercises
- Band Seated Low Rows
- Band Lat Pulldowns
- Band Deadlifts
- Single Leg Glute Bridges
- Band Bent Over Rows
Best Lower Back Workouts 1: Bodyweight and Bands
Warm-Up: Bodyweight Bird Dog: 3 sets of 8 to 15 reps
Band Glute Bridge: 3 x 8-12
Band Deadlifts: 3 x 8-12
Band Bent Over Rows: 3 x 8-12
Bodyweight Supermans: 3 sets x Failure (hold as long as you can)
Best Lower Back Workouts 2: Barbells and Dumbbells
Warm-Up: Single Arm Dumbbell Rows: 3 sets of 8 to 12 reps
Barbell Deadlifts: 3-4 x 8-12 reps
Barbell Rows – 3-4 x 8-12 reps
Best Lower Back Workouts 3: Mixed Equipment
Warm-Up: Bird Dogs: 3 sets of 8-15 reps
Rack Pulls – 3 sets x 8-12 reps
Seated Cable Rows – 3 sets x 12-15 reps
Dumbbell Aquaman: 3 x 8-12
The Relationship Between Sleep, Recovery, and Results
Getting enough sleep is incredibly important when it comes to seeing results from lower back exercises. After you break down the muscle fibers during a workout, they need time to rebuild and repair. This is why adequate rest and recovery are necessary for optimal gains.
It’s during sleep that the body produces hormones such as testosterone, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). These hormones play a critical role in recovery and muscle growth. Poor sleep equates to poor results because your body won’t have the building blocks it needs to repair muscle tissue, making it bigger and stronger for future workouts.
For best results, aim for at least seven hours of sleep per night. Don’t forget about adequate hydration and nutrition.
Best Supplements for Lower Back Muscle Growth and Recovery
Remember, the foundation of any muscle growth or strength-building goal is to focus on a well-balanced meal plan that provides healthy whole-food options. With that said, if your nutrition plan is on point, you can consider supplements to complement your nutrition.
Here are some of the best muscle-building supplements for the lower back. We also suggest you read the best pre-workout ingredients for strength and power.
Protein
Let’s kick this list off with the most obvious supplement for muscle and strength: protein!
Numerous studies show that whey protein directly supports muscle recovery and growth by increasing protein synthesis, protecting lean muscle tissue from breakdown, and providing amino acids, the building blocks of muscle.
Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound, but your body only makes so much and it’s quickly used up during the day. Supplementing with creatine increases strength, power output, and lean body mass. It’s also great for aiding muscle recovery.
Free-Form EAAs
As mentioned above, amino acids are the building blocks of muscle protein, and taking them can help you reduce muscle breakdown and support muscle recovery after a workout. Not all amino acids are the same. Essential amino acids are those that the body cannot make and must get through food or supplementation. In particular, studies show that leucine, isoleucine, and valine are the most effective essential amino acids for supporting recovery, strength, and growth.
Sleep Supplements (Melatonin)
As we mentioned above, healthy sleep is a non-negotiable if you want to recover and see great results. However, some of you might have trouble getting to sleep at a decent hour or staying asleep throughout the night. If you travel a lot, your sleep schedule might be completely out of whack.
One of the best ways to get on a better sleep schedule and stay asleep throughout the night is to take specific vitamins and minerals that promote sleep. Those include the following:
- Vitamin D
- Zinc
- Magnesium
- Vitamin B6
- Ashwagandha
- L-theanine
- GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid)
You can also take melatonin, but we would advise that you treat this more like a short-term solution and not rely on taking it every night for years.
While the other ingredients listed above are safe to take over the long term, melatonin should be taken for two or three weeks at most to assist with your sleep schedule. Taking high doses for long periods can impact your body’s natural ability to get to sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are the most commonly asked questions about lower back exercises for strength and muscle growth:
What’s the best lower back exercise for increasing mass?
The best lower back exercise for increasing mass is the deadlift, as it allows you to lift a heavy weight and increase your muscle size.
What’s the best lower back exercise for increasing strength?
One of the best exercises to strengthen lower back is the barbell row. This exercise allows you to lift heavier weight and challenge your muscles in a way that will lead to increased strength.
Which lower back exercises can I do at home?
There are plenty of lower back exercises you can do at home, such as bent-over barbell rows, single-arm dumbbell rows, and reverse flys. You can also use resistance bands for various lower back exercises.
Are there lower back exercises I can do with no equipment?
Yes! You can do many lower back exercises with bodyweight only, such as Supermans, bird dogs, and glute bridges. All these exercises will help strengthen and build the muscles in your lower back.
Are there any good lower back stretches?
Yes, several good lower back stretches can help you improve flexibility and reduce stiffness in your lower back muscles. These include the child’s pose, cobra pose, and lying spinal twist. You can do all of these stretches after a workout to help with recovery and prevent injury.
Will lower back exercises help with back pain?
Yes, certain lower back exercises can help alleviate and prevent back pain. These include core strengthening exercises such as planks, bridges, and Supermans. However, it’s best to speak with your doctor or physical therapist to understand which exercises are best for you.
Will my lower back get sore from exercise?
Yes, it is normal to experience some soreness in the lower back after exercise. However, if you are experiencing pain that doesn’t go away or gets worse over time, it’s best to speak with your doctor.
References
- Mangine GT, Hoffman JR, Gonzalez AM, Townsend JR, Wells AJ, Jajtner AR, Beyer KS, Boone CH, Miramonti AA, Wang R, LaMonica MB, Fukuda DH, Ratamess NA, Stout JR. The effect of training volume and intensity on improvements in muscular strength and size in resistance-trained men. Physiol Rep. 2015 Aug;3(8):e12472. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12472. PMID: 26272733; PMCID: PMC4562558.
- Plotkin D, Coleman M, Van Every D, Maldonado J, Oberlin D, Israetel M, Feather J, Alto A, Vigotsky AD, Schoenfeld BJ. Progressive overload without progressing load? The effects of load or repetition progression on muscular adaptations. PeerJ. 2022 Sep 30;10:e14142. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14142. PMID: 36199287; PMCID: PMC9528903.
- Krzysztofik M, Wilk M, Wojdała G, Gołaś A. Maximizing Muscle Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review of Advanced Resistance Training Techniques and Methods. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 4;16(24):4897. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244897. PMID: 31817252; PMCID: PMC6950543.
- Peterson MD, Pistilli E, Haff GG, Hoffman EP, Gordon PM. Progression of volume load and muscular adaptation during resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011 Jun;111(6):1063-71. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1735-9. Epub 2010 Nov 27. PMID: 21113614; PMCID: PMC4215195.
- Fonseca RM, Roschel H, Tricoli V, de Souza EO, Wilson JM, Laurentino GC, Aihara AY, de Souza Leão AR, Ugrinowitsch C. Changes in exercises are more effective than in loading schemes to improve muscle strength. J Strength Cond Res. 2014 Nov;28(11):3085-92. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000539. PMID: 24832974.
Author Bio
Related Posts:
- The Best Lat Exercises For Strength & Muscle Growth
- Best Muscle Pump Exercises For a Full Body Workout
- The Best Shoulder Workout for Hypertrophy
- Best Shoulder Exercises for Strength and Muscle Growth
- The Best Quad Exercises For Strength & Muscle Growth
- Best Strength Standards For Measuring Performance And Progress
